4.1.2.2. TCP粘包/拆包的基础知识
TCP是个流协议(没有界限的一串数据).底层并不了解上层业务数据,TCP会根据自身的缓冲区的实际情况进行包的划分。所以就有可能出现粘包/拆包问题;
4.1.2.2.1. 粘包
假设我们需要发送3次1 -> 服务器,理想中,服务器应该接收到3次1.
但是实际上有可能会一次接到111.这就是粘包。
4.1.2.2.2. 拆包
假设我们发送很3条大数据123456789,理想中,服务器应该接收到3次123456789.
但是实际情况上有可能只接到2次,一次接到123456789123,一次接到456789,这就是拆包。
4.1.2.2.3. TCP粘包/拆包发生的原因
- 应用程序write写入的自己大小大于套接接口发送缓冲区大小
- 进行MSS大小的TCP分段
- 以太网的帧
payload大于MTU进行IP分片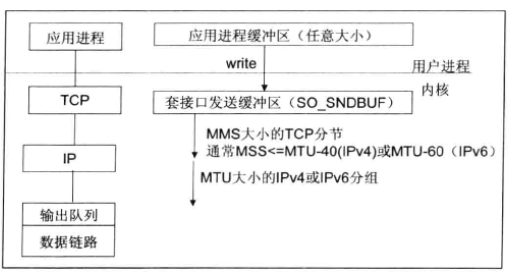
4.1.2.2.4. 粘包问题的解决策略
底层无法保证数据包的完整性,那么就通过上层应用协议栈来解决。主流的解决方案有:
- 消息定长。如:每个报文的大小为固定长度200字节,如果不够,空位补空格
- 在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割. 如:FTP协议
- 将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含表示消息总长度的字段,通常设计思路为消息头的第一个字段使用int32来标识消息的总长度。
- 更复杂的应用层协议。
4.1.2.2. 不考虑粘包/拆包案例
直接拿上面的入门例子改造。改造思路很简单。
- 在服务端统计下 读取的次数
在客户端连续发送100次
/** * 客户端和服务端TCP链路建立成功之后,该方法被调用 * @param ctx * @throws Exception */ @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // 主要更改这里。连续发送100条消息 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(req.length); firstMessage.writeBytes(req); ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage); } }
运行之后你会发现:(每个人的机器上测试的不同)
- 服务端只接收了5次,且每一次的信息 是好几条的合集,而且还有不完整的句子(中途被截断那种)
- 客户端只接收了一次。
明显的出现了问题。我们需要的是发送100次就接收100次
4.1.2.2. 使用Netty解决半包问题
首先我们要定制一个规则,在每行消息后面添加换行符。 再使用Netty提供的解决策略来解决。
+ System.getProperty("line.separator"); //使用系统换行符
// 刚才有粘包问题的加上换上符号结果也是一样的。
使用:LineBasedFrameDecoder 和 StringDecoder 解码器来解决问题;
需要注意的是:使用了解码器之后,接收到的消息就是已经是字符串了。不再是byte了。
public class TimeSrver {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8086;
new TimeSrver().bind(port);
}
public void bind(int port) throws InterruptedException {
// 配置服务端的NIO线程组
// 包含一组NIO线程,专门用于网络事件的处理
// 实际上他们就是Reactor线程组。
//用于接收客户端的链接
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
// 用于SocketChannel的网络读写
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
// 引导配置
ServerBootstrap starp = new ServerBootstrap();
try {
starp.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // 指定通道类型
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024) // 缓存大小?
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler()); // 绑定处理器
// 绑定端口,同步等待成功。 ChannelFuture: 类似Jdk.Future, 用于异步操作的通知回调
ChannelFuture channelFuture = starp.bind(port).sync();
// 等待服务器监听端口关闭。该方法会阻塞,链路关闭后,会被唤醒
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
//优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 增加解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHanler());
}
}
private int count = 0;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
private class TimeServerHanler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
count++;
log.info("== 请求消息:{}", msg);
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(("current time" + new Date().toString() + System.getProperty("line.separator")).getBytes());
ctx.write(resp); // 异步发送应答
log.error("== 接收次数:" + count);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 将消息发送队列中的消息写入到 SocketChannel中发送给对方
// 性能考虑,放置频繁唤醒Selector进行消息发送。
// Netty的方法并不直接将消息写入 SocketChannel中
// 调用write只是把消息放到了发送缓冲数组中。
// 通过flush方法将缓冲区中的消息全部写入到SocketChannel中
ctx.flush();
// 但是通过实际测试,在请求先进来的时候,会先执行该方法是什么原因呢?
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// 发生异常,释放相关句柄资源
ctx.close();
cause.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class TimeClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8086;
new TimeClient().connect("127.0.0.1", port);
}
public void connect(String host, int port) throws InterruptedException {
// 配置客户端NIO线程组
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 通道建立后,绑定我们的处理类
// 修改了这里,增加解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler());
}
});
// 发起异步链接操作
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
// 同步阻塞,链路关闭才被唤醒
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
//优雅退出,释放NIO线程组
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
private ByteBuf firstMessage;
byte[] req = {};
public TimeClientHandler() {
try {
req = (Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 发起请求" + "current time is ?" + new Date().toString() + System.getProperty("line.separator")).getBytes("UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
firstMessage.writeBytes(req);
}
/**
* 客户端和服务端TCP链路建立成功之后,该方法被调用
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 主要更改这里。连续发送100条消息
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
firstMessage.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage);
}
}
/**
* 服务端返回应答消息时,该方法被调用
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.info("== 接收到消息:{}", msg);
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
}
4.1.2.2.1. 原理解析
4.1.2.2.1.1. LineBasedFrameDecoder
一次遍历ByteBuf中的可读字节,判断是否有“\n”或则“\r\n”,如果有,就以此位置为结束位置,从可读索引到结束位置区间的字节就组成了一行。 它是以换行符为结束标志的解码器,支持携带结束符或不携带结束符两种解码方式,通知支持配置单行的最大长度。如果连续读取到最大长度后任然没有发现换行符,就会抛出异常,同时护绿掉之前独到的异常码流
4.1.2.2.1.2. StringDecoder
将接收到的对象转换成字符串,然后继续调用后面的Handler
LineBasedFrameDecoder 和 StringDecoder 组合就是按行切换的文本解码器。它被设计用来支持TCP的粘包和拆包。