# 将拉丁数字转换为其他 Unicode 数字
TIP
本章笔者由于对 awt 不熟悉,不太能看懂下面的代码,翻译的可能会没有什么头脑
默认情况下,当文本包含数值时,这些数值将使用拉丁(欧洲)数字显示。如果首选其他 Unicode 数字形状,请使用java.awt.font.NumericShaper 类。NumericShaper API 允许您显示在内部以任何 Unicode 数字形状表示的ASCII 值。
下面的代码片段展示了如何使用 NumericShaper 实例将 拉丁数字 转换 为阿拉伯数字。决定塑造动作的线是粗体的。
ArabicDigitsPanel(String fontname) {
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Font font = new Font(fontname, Font.PLAIN, 60);
map.put(TextAttribute.FONT, font);
// 这一句是使用了 NumericShaper 实例
map.put(TextAttribute.NUMERIC_SHAPING,
NumericShaper.getShaper(NumericShaper.ARABIC));
FontRenderContext frc = new FontRenderContext(null, false, false);
layout = new TextLayout(text, map, frc);
}
// ...
public void paint(Graphics g) {
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
layout.draw(g2d, 10, 50);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
通过 TextLayout.NUMERIC_SHAPING 获取阿拉伯数字的 NumericShaper 实例,并将其放入 TextLayout 的 HashMap 中。HashMap 被传递到 TextLayout 实例。在绘制方法中呈现文本后,数字将显示在所需的脚本中。
在本例中,拉丁数字( 0 到 9 ) 被绘制为阿拉伯数字。

该程序完整代码如下
package com.java;
/**
* This example displays ASCII digits, 0 through 9, as Arabit digits.
*/
import java.applet.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.font.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ArabicDigits extends Applet {
ArabicDigitsPanel panel;
static final String defaultFontName = "Lucida Sans";
public ArabicDigits() {
panel = new ArabicDigitsPanel(defaultFontName);
}
public ArabicDigits(String fontname) {
panel = new ArabicDigitsPanel(fontname);
}
public void init() {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add("Center", panel);
}
public void destroy() {
remove(panel);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
String fontname = defaultFontName;
if (args.length > 0) {
fontname = args[0];
}
ArabicDigits arabicDigits = new ArabicDigits(fontname);
arabicDigits.init();
arabicDigits.start();
Frame f = new Frame("ArabicDigits");
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
f.add("Center", arabicDigits);
f.setSize(600, 250);
f.setVisible(true);
}
public String getAppletInfo() {
return "Arabic Digits Example";
}
static class ArabicDigitsPanel extends Panel {
String fontname;
TextLayout layout;
private static final String text = "0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9";
void dumpChars(char[] chars) {
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; ++i) {
char c = chars[i];
if (c < 0x7f) {
System.out.print(c);
} else {
String n = Integer.toHexString(c);
n = "0000".substring(n.length()) + n;
System.out.print("0x" + n);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
ArabicDigitsPanel(String fontname) {
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Font font = new Font(fontname, Font.PLAIN, 60);
map.put(TextAttribute.FONT, font);
map.put(TextAttribute.NUMERIC_SHAPING,
NumericShaper.getShaper(NumericShaper.ARABIC));
FontRenderContext frc = new FontRenderContext(null, false, false);
layout = new TextLayout(text, map, frc);
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D) g;
layout.draw(g2d, 10, 50);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
# 基于枚举的范围常量
指定一组特定数字的另一种方法是使用 NumericShaper.Range 枚举类型(枚举)。这个枚举是在 Java SE 7 发行版中引入的,它还提供了一组常量。虽然这些常量是使用不同的机制定义的,但是 NumericShaper.ARABIC
阿拉伯语位掩码在功能上等同于 NumericShaper.Range。 NumericShaper.Range.ARABIC enum,每个常量类型都有对应的 getShaper 方法:
阿拉伯数字示例与阿拉伯数字示例相同,只是它使用了NumericShaper。指定语言脚本的范围枚举:
ArabicDigitsEnumPanel(String fontname) {
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Font font = new Font(fontname, Font.PLAIN, 60);
map.put(TextAttribute.FONT, font);
// 这里使用的是常量 NumericShaper.Range.ARABIC
map.put(TextAttribute.NUMERIC_SHAPING,
NumericShaper.getShaper(NumericShaper.Range.ARABIC));
FontRenderContext frc = new FontRenderContext(null, false, false);
layout = new TextLayout(text, map, frc);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
两个 getShaper 方法都接受一个单一参数。无论使用哪种常量类型,都可以指定特定于脚本的数字范围。
基于位掩码的常量可以使用 OR 操作数进行组合,也可以创建一组 NumericShaper.Range 枚举。下面展示了如何使用每种常量类型定义范围:
NumericShaper.MONGOLIAN | NumericShaper.THAI |
NumericShaper.TIBETAN
EnumSet.of(
NumericShaper.Range.MONGOLIAN,
NumericShaper.Range.THAI,
NumericShaper.Range.TIBETAN)
2
3
4
5
6
您可以查询 NumericShaper 对象来确定它支持哪些范围,使用 getRanges 方法(用于基于位掩码的塑形器)或getRangeSet 方法(用于基于枚举的塑形器)。
上面示例的完整代码是
package com.java;
/**
* This example displays ASCII digits, 0 through 9, as Arabit digits.
*/
import java.applet.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.font.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ArabicDigitsEnum extends Applet {
ArabicDigitsEnumPanel panel;
static final String defaultFontName = "Lucida Sans";
public ArabicDigitsEnum() {
panel = new ArabicDigitsEnumPanel(defaultFontName);
}
public ArabicDigitsEnum(String fontname) {
panel = new ArabicDigitsEnumPanel(fontname);
}
public void init() {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add("Center", panel);
}
public void destroy() {
remove(panel);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
String fontname = defaultFontName;
if (args.length > 0) {
fontname = args[0];
}
ArabicDigitsEnum arabicDigits = new ArabicDigitsEnum(fontname);
arabicDigits.init();
arabicDigits.start();
Frame f = new Frame("ArabicDigitsEnum");
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
f.add("Center", arabicDigits);
f.setSize(600, 250);
f.setVisible(true);
}
public String getAppletInfo() {
return "Arabic Digits Example";
}
static class ArabicDigitsEnumPanel extends Panel {
String fontname;
TextLayout layout;
private static final String text = "0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9";
void dumpChars(char[] chars) {
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; ++i) {
char c = chars[i];
if (c < 0x7f) {
System.out.print(c);
} else {
String n = Integer.toHexString(c);
n = "0000".substring(n.length()) + n;
System.out.print("0x" + n);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
ArabicDigitsEnumPanel(String fontname) {
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Font font = new Font(fontname, Font.PLAIN, 60);
map.put(TextAttribute.FONT, font);
map.put(TextAttribute.NUMERIC_SHAPING,
NumericShaper.getShaper(NumericShaper.Range.ARABIC));
FontRenderContext frc = new FontRenderContext(null, false, false);
layout = new TextLayout(text, map, frc);
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
layout.draw(g2d, 10, 50);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
他运行的结果和第一个实例的结果是一样的。
# 根据语言上下文渲染数字
ArabicDigits 例子(第一个示例)是设计用来为特定语言使用塑造器的,但是有时候必须根据语言上下文来呈现数字。例如,如果数字前面的文本使用泰文脚本,则首选泰文数字。如果文本以藏文显示,则首选藏文数字。
你可以使用 getContextualShaper 方法来完成这个任务:
- getContextualShaper(int ranges)
- getContextualShaper(int ranges, int defaultContext)
- getContextualShaper(Set ranges)
- getContextualShaper(Set ranges, NumericShaper.Range defaultContext)
前两个方法使用位掩码常量,后两个方法使用枚举常量。接受 defaultContext 参数的方法使您能够指定在文本前面显示数值时使用的初始塑造器。如果没有定义缺省上下文,则使用拉丁形状显示任何前导数字。
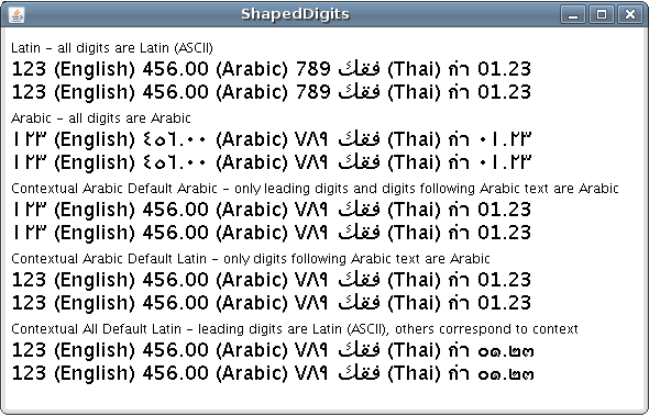
下面的例子显示了形状器是如何工作的。五个文本布局显示:
- 第一个布局没有使用shaper;所有的数字都显示为拉丁文。
- 第二种布局将所有数字设置为阿拉伯数字,与语言上下文无关。
- 第三种布局使用使用阿拉伯数字的上下文塑形器。默认上下文被定义为阿拉伯语。
- 第四个布局使用使用阿拉伯数字的上下文构造器,但是构造器没有指定默认上下文。
- 第五个布局使用上下文塑造器,它使用 ALL_RANGES 位掩码,但是这个塑造器没有指定默认上下文。
下面的代码行显示了如何定义塑形器(如果使用的话):
- No shaper is used.
NumericShaper arabic = NumericShaper.getShaper(NumericShaper.ARABIC);NumericShaper contextualArabic = NumericShaper.getContextualShaper(NumericShaper.ARABIC, NumericShaper.ARABIC);NumericShaper contextualArabicASCII = NumericShaper.getContextualShaper(NumericShaper.ARABIC);NumericShaper contextualAll = NumericShaper.getContextualShaper(NumericShaper.ALL_RANGES);
完整代码如下
package com.java;
import java.applet.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.font.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ShapedDigits extends Applet {
ShaperPanel panel;
static final String defaultFontName = "Lucida Sans";
public ShapedDigits() {
panel = new ShaperPanel(defaultFontName);
}
public ShapedDigits(String fontname) {
panel = new ShaperPanel(fontname);
}
public void init() {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add("Center", panel);
}
public void destroy() {
remove(panel);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
String fontname = defaultFontName;
if (args.length > 0) {
fontname = args[0];
}
ShapedDigits shapedDigits = new ShapedDigits(fontname);
shapedDigits.init();
shapedDigits.start();
Frame f = new Frame("ShapedDigits");
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
f.add("Center", shapedDigits);
f.setSize(600, 250);
f.setVisible(true);
}
public String getAppletInfo() {
return "Shaped Digits Sample";
}
static class ShaperPanel extends Panel {
String fontname;
TextLayout[][] layouts;
String[] titles;
private static final String text =
"-123 (Latin) 456.00 (Arabic) \u0641\u0642\u0643 -789 (Thai) \u0e01\u0e33 01.23";
void dumpChars(char[] chars) {
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; ++i) {
char c = chars[i];
if (c < 0x7f) {
System.out.print(c);
} else {
String n = Integer.toHexString(c);
n = "0000".substring(n.length()) + n;
System.out.print("0x" + n);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
ShaperPanel(String fontname) {
setBackground(Color.white);
setForeground(Color.black);
Font textfont = new Font(fontname, Font.PLAIN, 12);
System.out.println("asked for: " + fontname + " and got: " + textfont.getFontName());
setFont(textfont);
Font font = new Font(fontname, Font.PLAIN, 18);
System.out.println("asked for: " + fontname + " and got: " + font.getFontName());
FontRenderContext frc = new FontRenderContext(null, false, false);
layouts = new TextLayout[5][2];
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put(TextAttribute.FONT, font);
layouts[0][0] = new TextLayout(text, map, frc);
AttributedCharacterIterator iter = new AttributedString(text, map).getIterator();
layouts[0][1] = new LineBreakMeasurer(iter, frc).nextLayout(Float.MAX_VALUE);
NumericShaper arabic = NumericShaper.getShaper(NumericShaper.ARABIC);
map.put(TextAttribute.NUMERIC_SHAPING, arabic);
layouts[1][0] = new TextLayout(text, map, frc);
iter = new AttributedString(text, map).getIterator();
layouts[1][1] = new LineBreakMeasurer(iter, frc).nextLayout(Float.MAX_VALUE);
NumericShaper contextualArabic = NumericShaper.getContextualShaper(NumericShaper.ARABIC, NumericShaper.ARABIC);
map.put(TextAttribute.NUMERIC_SHAPING, contextualArabic);
layouts[2][0] = new TextLayout(text, map, frc);
iter = new AttributedString(text, map).getIterator();
layouts[2][1] = new LineBreakMeasurer(iter, frc).nextLayout(Float.MAX_VALUE);
NumericShaper contextualArabicASCII = NumericShaper.getContextualShaper(NumericShaper.ARABIC);
map.put(TextAttribute.NUMERIC_SHAPING, contextualArabicASCII);
layouts[3][0] = new TextLayout(text, map, frc);
iter = new AttributedString(text, map).getIterator();
layouts[3][1] = new LineBreakMeasurer(iter, frc).nextLayout(Float.MAX_VALUE);
NumericShaper contextualAll = NumericShaper.getContextualShaper(NumericShaper.ALL_RANGES);
map.put(TextAttribute.NUMERIC_SHAPING, contextualAll);
layouts[4][0] = new TextLayout(text, map, frc);
iter = new AttributedString(text, map).getIterator();
layouts[4][1] = new LineBreakMeasurer(iter, frc).nextLayout(Float.MAX_VALUE);
titles = new String[]{
"Latin - all digits are Latin (ASCII)",
"Arabic - all digits are Arabic",
"Contextual Arabic Default Arabic - only leading digits and digits following Arabic text are Arabic",
"Contextual Arabic Default Latin - only digits following Arabic text are Arabic",
"Contextual All Default Latin - leading digits are Latin (ASCII), others correspond to context"
};
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D) g;
float x = 5;
float y = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < layouts.length; ++i) {
y += 18;
g2d.drawString(titles[i], x, y);
y += 4;
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j) {
y += layouts[i][j].getAscent();
layouts[i][j].draw(g2d, x, y);
y += layouts[i][j].getDescent() + layouts[i][j].getLeading();
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153