# 栈快速入门
# 计算器需求

如上图:输入一个表达式 7*2*2-5+1-5+3-3,然后计算出他的结果。
问:计算机底层是如何运算得到结果的?对于计算机而言他接受到的是一个 字符串,怎么计算出来的?
针对这个问题,我们讨论的就是 栈
# 栈介绍
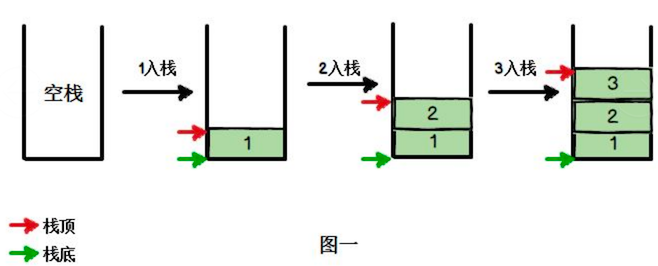
stack 栈,是一个 先入后出(FILO,First In Last Out)的 有序列表。
是限制 线性表 中元素的插入和删除只能在线性表的 **同一端 **进行的一种特殊线性表:
- 栈顶(Top):允许插入和删除的一端,为 变化的一端。称为栈顶
- 栈底(Bottom):另一端为 固定的一端,称为栈底
根据上述定义,可知:
- 最先 放入栈中元素在 栈底
- **最后 **放入栈中元素在 栈顶
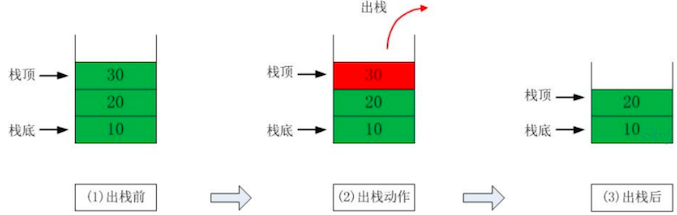
而删除元素则刚好相反:
- 最先 放入栈中元素,最后 删除
- 最后 放入栈中元素,最先 删除
可以参考下图的,入栈和出栈图示:
# 栈的应用场景
子程序的调用
在跳往子程序前,会先将 下个指令的地址 存到堆栈中,直到子程序执行完后再 将地址取出,以 回到原来的程序中。
如方法中调用方法。
处理递归调用
和子程序调用类似,只是除了存储下一个指令的地址外,也将参数、区域变量等数据存入堆栈中。
表达式的转换(中缀表达式转后缀表达式)与求值(实际解决)
二叉树的遍历
图形的深度优先(depth-first)搜索法
# 数组模拟栈
参考前面的入栈和出栈的图,思路如下:
- 定义一个数组,来模拟栈
- 定义一个 top 变量表示栈顶,初始化为
-1 - 入栈:
stack[++top]=data - 出栈:
return stack[top--]
package cn.mrcode.study.dsalgtutorialdemo.datastructure.stack.array;
/**
* 数组模拟栈
*/
public class ArrayStack {
int[] stack; // 数据存储
int maxSize; // 栈最大数量
int top = -1; // 栈顶位置
public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[maxSize];
}
/**
* 是否已满
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return maxSize - 1 == top;
}
/**
* 是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
/**
* 入栈
*
* @param value
*/
public void push(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈已满");
return;
}
stack[++top] = value;
}
/**
* 出栈
*
* @return
*/
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈中无数据");
}
return stack[top--];
}
/**
* 显示栈中数据,从栈顶开始显示,也就是按出栈的顺序显示
*/
public void print() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈中无数据");
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.printf("index=%d, value=%d \n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
测试用例
package cn.mrcode.study.dsalgtutorialdemo.datastructure.stack.array;
import org.junit.Test;
public class ArrayStackTest {
@Test
public void pushTest() {
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(4);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.print();
stack.push(5);
}
@Test
public void popTest() {
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(4);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.print();
System.out.println("pop 数据:" + stack.pop());
stack.print();
System.out.println("pop 数据:" + stack.pop());
stack.print();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
输出信息
====== pushTest
index=1, value=2
index=0, value=1
pop 数据:2
index=0, value=1
pop 数据:1
栈中无数据
====== popTest
index=3, value=4
index=2, value=3
index=1, value=2
index=0, value=1
栈已满
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 链表模拟栈
课堂作业:使用链表模拟栈,加深印象。
package cn.mrcode.study.dsalgtutorialdemo.datastructure.stack.linkedlist;
/**
* 链表实现栈; 单向链表
*/
public class LinkedListStack {
int maxSize; // 最大支持数
int size; // 当前栈中元素个数
// 用来记录栈顶的元素
Node top;
public LinkedListStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
/**
* 是否已满
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return size == maxSize;
}
/**
* 是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* 入栈
*
* @param value
*/
public void push(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈已满");
return;
}
// 要保证 top 是最后进来的
Node temp = top;
top = new Node(value);
top.next = temp;
size++;
}
/**
* 出栈
*
* @return
*/
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈已空");
}
// top 保存的是最后入栈的元素,直接从 top 取出即可
Node temp = top;
top = temp.next;
size--;
return temp.value;
}
/**
* 显示栈中数据,从栈顶开始显示,也就是按出栈的顺序显示
*/
public void print() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈已空");
return;
}
Node cur = top;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.println(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node next;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"value=" + value +
'}';
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
测试用例,和数组测试用例一模一样,只是更换了栈
package cn.mrcode.study.dsalgtutorialdemo.datastructure.stack.linkedlist;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* 链表实现栈
*/
public class LinkedListStackTest {
@Test
public void pushTest() {
LinkedListStack stack = new LinkedListStack(4);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.print();
stack.push(5);
}
@Test
public void popTest() {
LinkedListStack stack = new LinkedListStack(4);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.print();
System.out.println("pop 数据:" + stack.pop());
stack.print();
System.out.println("pop 数据:" + stack.pop());
stack.print();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
测试输出
====== pushTest
Node{value=4}
Node{value=3}
Node{value=2}
Node{value=1}
栈已满
====== popTest
Node{value=2}
Node{value=1}
pop 数据:2
Node{value=1}
pop 数据:1
栈已空
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
← 栈 综合计算器-中缀表达式 →