# 基准测试案例
本章使用上面提到的部分共计进行测试,告诉你怎么入门
# http_load
首先创建一个 urls.txt 文件,输入如下的 RUL
http://www.mysqlperformanceblog.com/
http://www.mysqlperformanceblog.com/page/2/
http://www.mysqlperformanceblog.com/mysql-patches/
http://www.mysqlperformanceblog.com/mysql-performance-presentations/
http://www.mysqlperformanceblog.com/2006/09/06/slow-query-log-analyzes-tools/
2
3
4
5
最简单的用法,就是循环请求给定的 URL 列表。测试程序将以最快的速度请求这些 URL
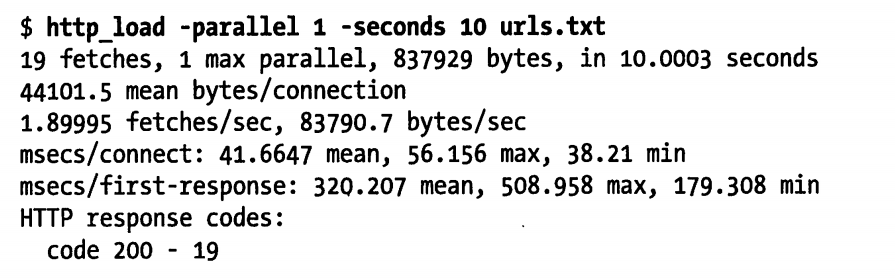
测试的结果很容易理解,只是简单的输出了请求的统计信息。下面是一个稍微复杂的测试,模拟同时有 5 个用户在进行请求
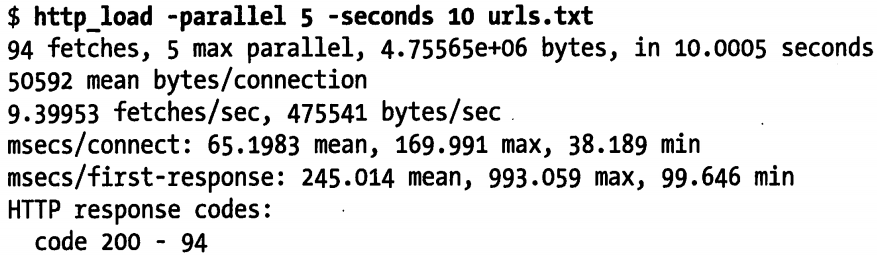
另外,除了测试最快的速度,有可以根据预估的访问请求率(比如每秒 5 次)来做压力模拟测试
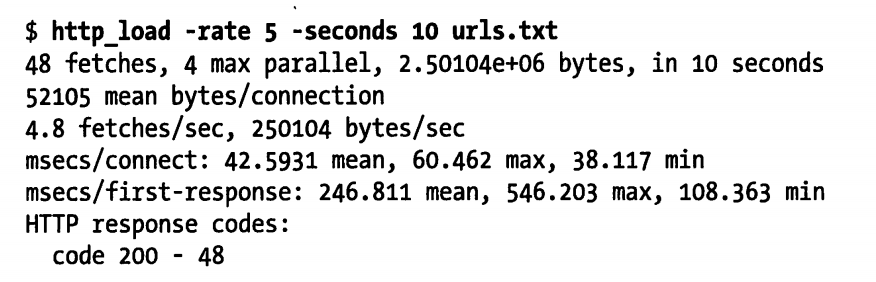
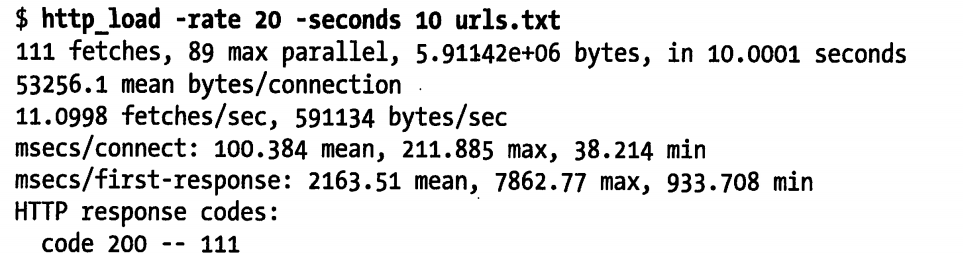
最后,还可以模拟更大的负载,可以将访问请求率提高到每秒 20 次请求。请注意,连接和请求响应时间都会随着负载的提高而增加
# MySQL 基准测试套件
MySQL Benchmark Suite 由一组基于 Perl 开发的基准测试工具组成。在 MySQl 安装目录下的 sql-bench 子目录中包含了该工具。Linux 系统上,默认的路径是 /usr/share/mysql/sql-bench
笔者装的 MySQL 8.0 ,没有找到该工具。下面截图
可以阅读该工具的 README 文件,了解使用方法和命令行参数说明。如果要运行全部测试,可以使用如下的命令
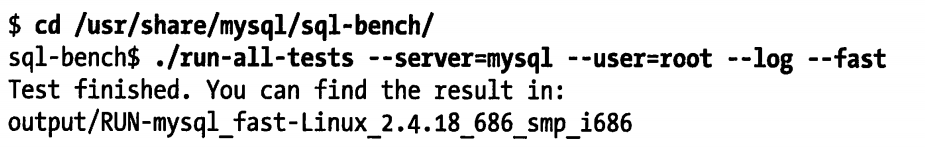
执行时间很正常,可能会超过一小时。如果指定了 --log 命令行,则可以监控到测试的进度。测试的结果都保存在 output 子目录中,每项测试的结果文件都会包含一系列的操作计时信息。下面是一个具体的例子
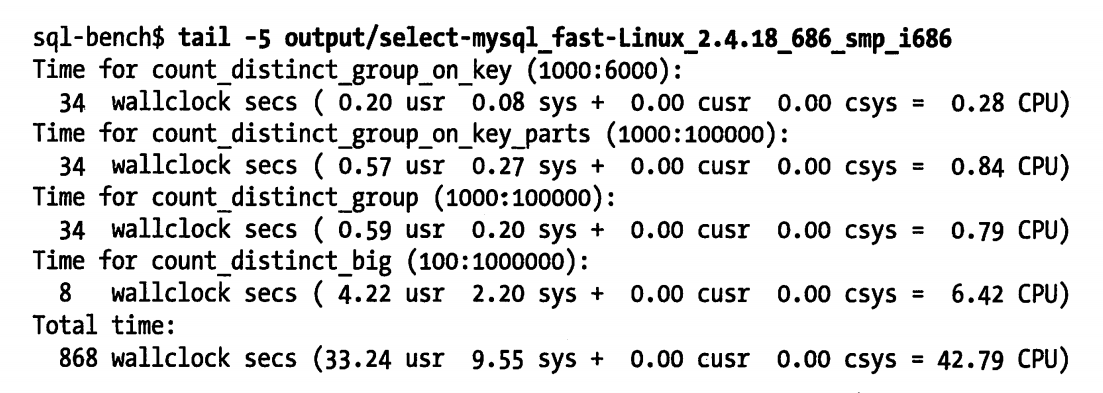
如上所示: count_distinct_group_one_key(1000:6000) 测试花费了 34 秒(wallclock secs),这是客户端运行测试花费的总时间,其他值(usr、sys、cursr、csys)则占了测试的 0.28 秒的开销,这是运行客户端测试代码所花费的时间,而不是等待 MySQL 服务器响应的时间。而测试者正在需要关心的测试结果,是除去客户端控制的部分,即实际运行时间应该是 33.72 秒
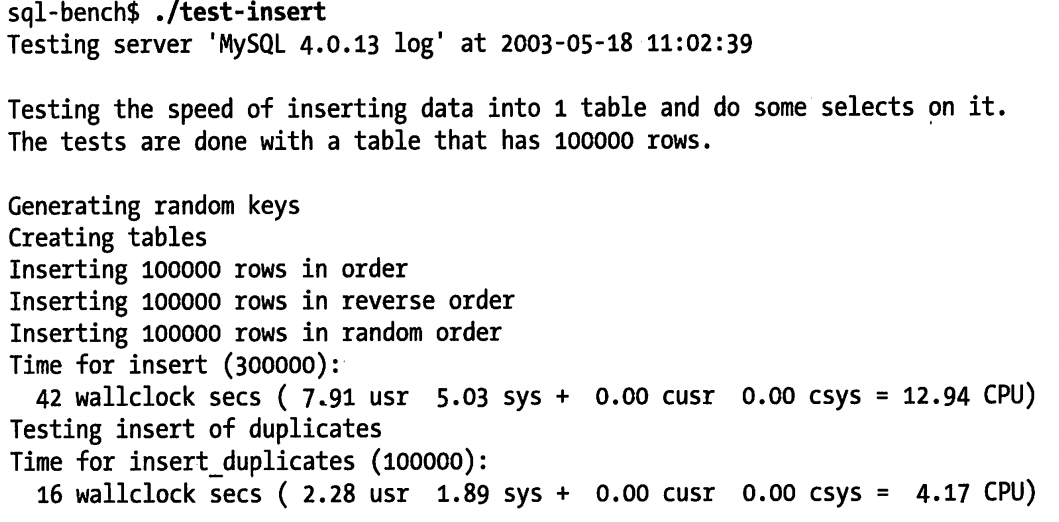
还可以选择单独执行其中的部分测试项,例如可以选择只执行 insert 测试
# sysbench
sysbench ky 可以执行多种类型的基准测试,不仅用来测试数据库的性能,也可以测试运行数据库的服务器性能。 实际上,peter 和 vadim 最初设计这个工具是用来执行 MySQL 性能测试的(尽管并不能完成所有的 MySQL 基准测试)。下面先演示一些非 MySQL 的测试场景,来测试各个子系统的性能,这些测试可以用来评估系统的整体性能瓶颈。后面在演示如何测试数据库的性能
建议大家都熟悉该工具,在 MySQL 用户的工具包中,这一个是最有用的工具之一。有替代他的某些功能,但是那些工具并不靠谱,获得的结果也不一定和 MySQL 性能相关。例如 I/O 性能测试可以用 iozone、bonnie++ 等工具,但需要注意设计场景,以便可以模拟 InnoDB 的磁盘 I/O 模式。 而 sysbench 的 I/O 测试和 InnoDB 的 I/O 模式非常类似,所以 fileio 选项是非常好用的
# centos 7 下安装该软件
yum -y install make automake libtool pkgconfig libaio-devel vim-common
# 安装方式来自 https://github.com/akopytov/sysbench#installing-from-binary-packages
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/akopytov/sysbench/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
sudo yum -y install sysbench
2
3
4
5
6
# sysbench 的 CPU 基准测试
[root@study yum.repos.d]# sysbench --test=cpu --cpu-max-prime=20000 run
WARNING: the --test option is deprecated. You can pass a script name or path on the command line without any options.
sysbench 1.0.20 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta2)
Running the test with following options:
Number of threads: 1
Initializing random number generator from current time
Prime numbers limit: 20000
Initializing worker threads...
Threads started!
CPU speed:
events per second: 534.88
General statistics:
total time: 10.0011s # 这里是计算的总时间数
total number of events: 5350
Latency (ms):
min: 1.81
avg: 1.87
max: 32.18
95th percentile: 1.93
sum: 9996.15
Threads fairness:
events (avg/stddev): 5350.0000/0.00
execution time (avg/stddev): 9.9961/0.00
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
可以通过这个去测试多台不同的计算机的性能。
# sysbench 的文件 I/O 基准测试
文件 I/O(fileio)基准测试可以测试系统在不同 I/O 负载下的性能。这对于比较不同的硬盘驱动器、不同的 RAID卡、不同的 RAID 模式,都很有帮助。可以根据测试结果来调整 I/O 子系统。文件 I/O 基准测试模拟了很多 InnoDB 的 I/O 特性。
测试的第一步是准备(prepare)阶段,生成测试用到的数据文件,文件只要要比内存大。否则全部可以放入内存中,则无法体现 I/O 密集型的工作负载。通过下面的命令创建一个数据集
sysbench --test=fileio --file-total-size=20G prepare
WARNING: the --test option is deprecated. You can pass a script name or path on the command line without any options.
sysbench 1.0.20 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta2)
128 files, 163840Kb each, 20480Mb total
Creating files for the test...
Extra file open flags: (none)
...
Creating file test_file.47
Creating file test_file.48
Creating file test_file.49
...
# 会生成很多小文件。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
该命令会在当前工作目录下创建测试文件,后续的运行(run)阶段将通过读写这些文件进行测试。针对不同的 I/O 类型有不同的测试选项:
- seqwr:顺序写入
- seqrewr:顺序重写
- seqrd:顺序读取
- rndrd:随机读取
- rndwr:随机写入
- rdnrw:混合随机读/写
下面的命令运行文件 I/O 混合随机读写基准测试
# 总时间是测试 300 秒
$ sysbench --test=fileio --file-total-size=20G --file-test-mode=rndrw --max-time=300 --max-requests=0 run
WARNING: the --test option is deprecated. You can pass a script name or path on the command line without any options.
WARNING: --max-time is deprecated, use --time instead
sysbench 1.0.20 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta2)
Running the test with following options:
Number of threads: 1
Initializing random number generator from current time
Extra file open flags: (none)
128 files, 160MiB each
20GiB total file size
Block size 16KiB
Number of IO requests: 0
Read/Write ratio for combined random IO test: 1.50
Periodic FSYNC enabled, calling fsync() each 100 requests.
Calling fsync() at the end of test, Enabled.
Using synchronous I/O mode
Doing random r/w test
Initializing worker threads...
Threads started!
File operations: # 文件操作
reads/s: 660.30 # 每秒读取 660.30 次
writes/s: 440.20
fsyncs/s: 1408.95
Throughput: # 吞吐量
read, MiB/s: 10.32 # 每秒 10.32 Mb
written, MiB/s: 6.88
General statistics:
total time: 300.0432s # 总测试时间
total number of events: 752818
Latency (ms):
min: 0.00
avg: 0.40
max: 841.22
95th percentile: 0.84 # 95% 的时间分布
sum: 299415.63
Threads fairness:
events (avg/stddev): 752818.0000/0.00
execution time (avg/stddev): 299.4156/0.00
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
测试完成后,运行清除(cleanup)操作删除第一步生成的测试文件
[root@study test]# sysbench --test=fileio --file-total-size=20G cleanup
WARNING: the --test option is deprecated. You can pass a script name or path on the command line without any options.
sysbench 1.0.20 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta2)
Removing test files...
2
3
4
5
6
# sysbench 的 OLTP 基准测试
OLTP 基准测试模拟了一个简单的事物处理系统的工作负载。下面的例子使用的是一张超过百万行记录的表,第一步是先生成这张表
[root@study test]# sysbench --test=oltp --oltp-table-size=1000000 --mysql-db=test --mysql-user=root prepare
WARNING: the --test option is deprecated. You can pass a script name or path on the command line without any options.
sysbench 1.0.20 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta2)
FATAL: Cannot find benchmark 'oltp': no such built-in test, file or module
# 笔者执行后报错,应该是 sysbench 版本的太高的问题。下面还是截图
# 后补:该软件不能和 mysql8 安装在一台机器上,会有冲突
2
3
4
5
6
7
8

下列例子采用了 8 个并发线程,只读模式,测试时间为 60 秒
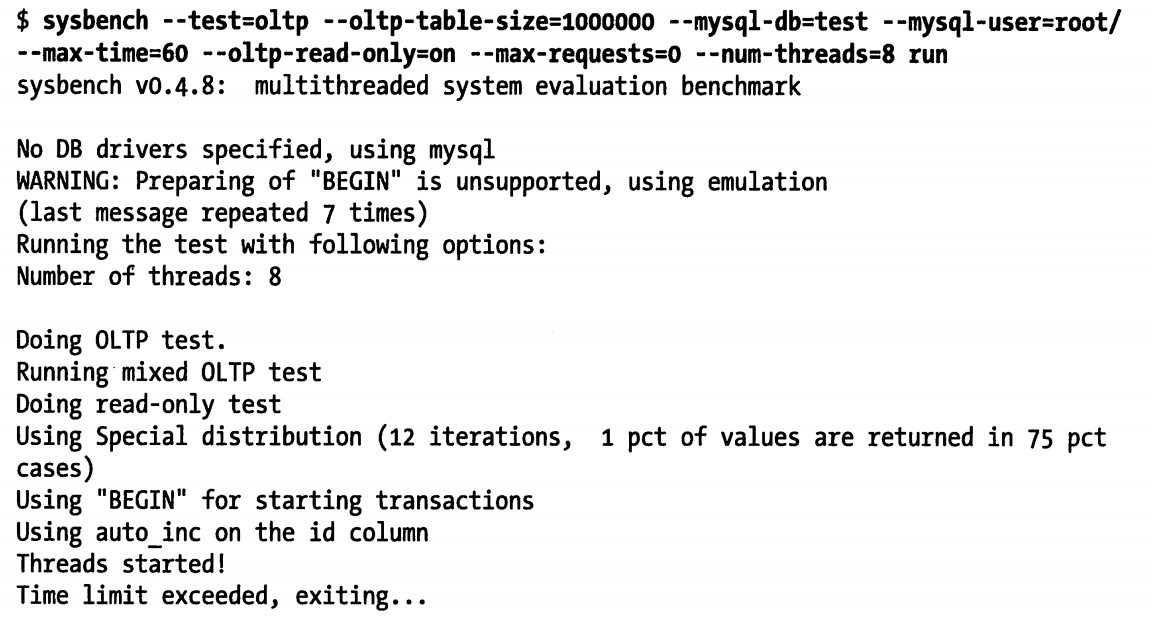
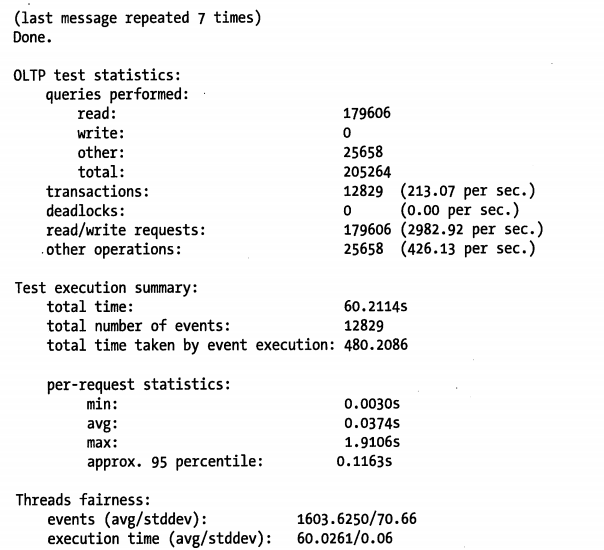
如上所示,结果中包含了相当多的信息,其中最有价值的信息如下:
- 总的事物数
- 每秒事物数
- 时间统计信息(最小、平均、最大响应时间,以及 95% 百分比响应时间)
- 线程公平性统计信息(thread-fairness),用于标识模拟负载的公平性
# sysbench 的其他特性
还有一些其他的基准测试,但和数据库性能没有直接关系
内存(memory):测试内存的连续读写性能
线程(thread):测试线程调度器的性能。对于高负载情况下测试线程调度器的行为非常有用。
互斥锁(mutex)
测试互斥锁的性能,方式是模拟所有线程在同一时刻并发运行,并都短暂请求互斥锁(互斥锁 mutex 是一种数据结构,用来对某些资源进行排他性访问控制,防止因并发访问导致问题。)
顺序写(seqwr)
测试顺序写的性能。这对于测试系统的实际性能瓶颈很重要。可以用来测试 RAID 控制器的高速缓存的性能状况,如果测试结果异常则需要引起重视。例如,如果 RAID 控制器写缓存没有电池保护,而磁盘的压力达到了 3000 次请求/秒,就是一个问题,数据可能是不安全的
另外,除了制定测试模式参数(--test)外,还有其他很多参数,比如 --num、--threads、--max-requests、--max-time 参数,更多信息请查阅官网文档。
# 数据库测试套件中的 dbt2 TPC-C 测试
数据库测试套件(Database Test Suite)中的 dbt2 是一款免费的 TPC-C 测试工具。 TPC-C 是 TPC 组织发布的一个测试规范,用于模拟测试复杂的在线事物处理系统(OLTP)。它的测试结果包括每分钟事物数(tpmC),以及每事物的成本(Price/tpmC)。这种测试的结果非常依赖硬件环境,所以公开发布的 TPC-C 测试结果都会包含具体的系统硬件配置信息。
笔者不想看这个了,看了前面的都是一头雾水
# Percona 的 TPCC-MySQL 测试工具
笔者不想阅读这个了。并且这个本书用的工具都太老的,对于笔者 2020 年才阅读的这书籍