# nginx.conf 配置详解
再次说明下!
这些基础的东西在官方文档里面都有详细的说明 http://nginx.org/en/docs/
笔者就是有时候看的东西多了,某些软件的文档讲的特别的不好,所以有时候会先入为主,觉得看不懂官方文档,其实 nginx 的文档还不错,下面讲的这些在文档里面都有详细的讲解
nginx 中的指令都可以在这个 官方页面 (opens new window) 中找到
# nginx.conf 文件结构
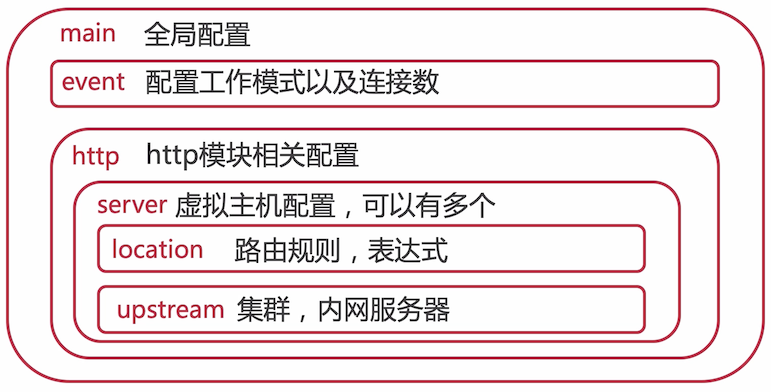
# 一条指令,由分号结尾
worker_processes 1;
# 花括号的为指令块,里面包含多个指令块
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
# 由 $ 符号开头的是 nginx 内置的一些变量
# log_format main '$remote_addr ....'
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# 指令之间由至少一个空格进行分割
# 也可以使用 tap,一个 tap 表示 8 个空格,但是一般使用 4 个空格缩进比较好
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 指令详解
下面针对默认配置文件中的内容进行一个详解
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
# user
user nobody:由操作系统的哪一个用户来执行指令
[root@study conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx
root 10108 1 0 16:31 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx
nobody 10965 10108 0 17:27 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
2
3
可以看到 worker 是 nobody 运行的,而 master 是 root,是因为 nginx 是我们主动运行的。
不同用户的进程,它对于操作系统的权限是不一样的(最明显的是文件的权限)
# worker_processes
配置几个 worker 服务,一般配置为 CPU 核心数,或则未核心数 减 1
# error_log
配置错误的日志,文件后面的为日志级别
error_log logs/error.log;
error_log logs/error.log notice;
error_log logs/error.log info;
2
3
日志级别从低到高分别是:debug、info、notice、warn、error、crit
默认日志文件地址在我们安装的时候通过 --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/xx.log 指定了,我们不配置的话,它自己也有默认文件地址的
# pid
运行时的进程 ID 文件
# events
events {
# 默认使用 epoll,在 linux 下最合适的就是 epoll,其他平台上可能不一样
use epoll;
# 每个 worker 允许连接的客户端最大连接数
worker_connections 1024;
}
2
3
4
5
6
# http
网络传输相关的模块,是一个指令块
# include
include mime.types;
在 nginx.conf 同级目录下,有一个 mime.types 文件,里面也是一个指令块内容,包含了很多的 mime type
[root@study conf]# cat mime.types
types {
text/html html htm shtml;
text/css css;
text/xml xml;
image/gif gif;
...
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
同理,include 就可以导入你自己的其他配置文件了,通过它来进行分类重用之类的工作
# log_format
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
2
3
4
5
需要配合 access_log 使用,log_format 是日志格式的指定,记录的是 http 请求相关的日志信息
[root@study conf]# cat /var/log/nginx/access.log
192.168.56.1 - - [04/Apr/2021:16:32:44 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_2_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36"
192.168.56.1 - - [04/Apr/2021:16:32:44 +0800] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 555 "http://192.168.56.105/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_2_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36"
2
3
如上所以的日志格式,就是被注释的默认格式所格式化出来的
remote_addr:ip 地址remote_user:远程用户,一般都是横杠-表示无法获取time_local:访问时间request:访问方法和地址还有协议status:响应状态body_bytes_sent:响应内容的大小http_referer:用是从哪一个链接跳转过来的http_user_agent:用户代理,一般写的浏览器http_x_forwarded_for:客户端 IP,通过代理转发后的 IP
# sendfile
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
2
文件高效传输,而 tcp_nopush 需要配合 sendfile 一起使用,含义是:当数据包内容累积到一定大小的时候才会发送,相当于是定义缓存
# keepalive_timeout
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
2
客户端链接服务端超时的时间,http 协议里面的东西,保持长链接的空闲时间,这里单位是秒
# gzip
#gzip on;
gzip 压缩开关
# server
server 也就是虚拟主机
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
- listen:监听端口
- server_name:可以定义 IP 或则域名
- location:路由
- error_page:发生错误的时候,使用这里响应的状态码页面展示
# pid 打开失败及解决方案
[root@study nginx]# ./sbin/nginx -s reload
nginx: [error] open() "/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid" failed (2: No such file or directory)
2
其实打开这个文件失败,解决办法呢,就是先去看看这个路径的文件是否存在:
如果是
/var/run/nginx/不存在,则创建这个目录就好了mkdir /var/run/nginx/1目录存在之后,再次尝试重启,报错 pid 无效
./sbin/nginx -s reload nginx: [error] invalid PID number "" in "/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid"1
2解决如下
[root@study nginx]# ./sbin/nginx -h nginx version: nginx/1.16.1 Usage: nginx [-?hvVtTq] [-s signal] [-c filename] [-p prefix] [-g directives] Options: -?,-h : this help -v : show version and exit -V : show version and configure options then exit -t : test configuration and exit -T : test configuration, dump it and exit -q : suppress non-error messages during configuration testing -s signal : send signal to a master process: stop, quit, reopen, reload -p prefix : set prefix path (default: /usr/local/nginx/) -c filename : set configuration file (default: conf/nginx.conf) -g directives : set global directives out of configuration file1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16查看下 nginx 的帮助,看到有一个
-c的选项,手动选择配置文件./sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf # 再次重启就可以了 ./sbin/nginx -s reload1
2
3
4TIP
nginx 在运行期间,这个 pid 文件丢失的话,就会出现上面的情况,执行信号指令就会报错,这个时候就只能先 kill 掉 master 进程,再手动指定下配置文件运行后,就可以了。
这个 pid 文件只有在运行时才会产生
# 常用命令解析
stop:暴力停止类似 kill
./nginx -s stopquit:优雅的关闭,有连接存在的话,会等待连接释放后再关闭,同时不再接受新的请求,仅针对 http 请求有效
./nginx -s quit-t:测试验证配置文件是否有问题./nginx -t-v:nginx 版本号./nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.16.11
2-V:可以将编译时的配置参数大打印出来./nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.16.1 built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC) configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --with-http_gzip_static_module --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/client --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/proxy --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/fastcgi --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/uwsgi --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/scgi1
2
3
4-c:指定配置文件./nginx -c /usr/con/con.conf1
# Nginx 日志切割-手动
前面配置了 nginx 的日志文件路径 /var/log/nginx/access.log,随着时间的增加,日志内容会越来越多,不方便查看,可以以时间为单位将文件进行切割
- 创建 shell 脚本文件
cut_my_log.sh
#!/bin/bash
LOG_PATH="/var/log/nginx/"
RECORD_TIME=$(date -d "yesterday" +%Y-%m-%d+%H:%M)
PID=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid
mv ${LOG_PATH}/access.log ${LOG_PATH}/access.${RECORD_TIME}.log
mv ${LOG_PATH}/error.log ${LOG_PATH}/error.${RECORD_TIME}.log
#向Nginx主进程发送信号,用于重新打开日志文件
kill -USR1 `cat $PID`
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
添加可执行权限
chmod u+x cut_my_log.sh1执行脚本,查看结果
./cut_my_log.sh # 检查结果:可以看到按时间命名了 ll /var/log/nginx/ 总用量 8 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 428 4月 4 16:32 access.2021-04-03+22:02.log -rw-r--r-- 1 nobody root 0 4月 4 22:02 access.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2143 4月 4 21:15 error.2021-04-03+22:02.log -rw-r--r-- 1 nobody root 0 4月 4 22:02 error.log1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
生成的文件名是这句代码 RECORD_TIME=$(date -d "yesterday" +%Y-%m-%d+%H:%M),这里是按照分为单位生成的,可以修改它按天、小时之类的切割
# Nginx 日志切割-定时
使用 crontab 来定时执行脚本,某些 linux 已经自带了,如果没有自带可以安装再配置
# 安装
yum instal crontabs
# crontab -e 增加下面一行配置,文件使用绝对路径指向刚刚的脚本文件
*/1 * * * * /usr/local/nginx/sbin/cut_my_log.sh
# 重启定时任务
service crond restart
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
定时任务的常用命令:
service crond start //启动服务 service crond stop //关闭服务 service crond restart //重启服务 service crond reload //重新载入配置 crontab -e // 编辑任务 crontab -l // 查看任务列表
定时任务表达式:
Cron表达式是,分为5或6个域,每个域代表一个含义,如下所示:
| 分 | 时 | 日 | 月 | 星期几 | 年(可选) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 取值范围 | 0-59 | 0-23 | 1-31 | 1-12 | 1-7 | 2019/2020/2021/… |
如:
# 每分钟执行
*/1 * * * *
# 每日凌晨(每天晚上23:59)执行:
59 23 * * *
# 每日凌晨1点执行
0 1 * * *
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 配置 Nginx 为静态资源提供服务
发布静态资源作为一个服务,供用户使用
我们可以这样做,创建一个 /usr/local/nginx/conf/my.conf 的文件,里面写指令,再在默认的配置文件里面 include 进去,分离我们自己的脚本文件的方式来组织配置
my.conf
server {
listen 90;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /home/foodie-shop/;
index index.html;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
在默认的配置文件中 include 我们的配置文件
http {
...
include my.conf;
...
2
3
4
重新加载 nginx
./nginx -s reload
以上配置,我们将我们前端项目使用 nginx 部署了,这个时候可以访问 http://192.168.56.105:90/ 就能访问到前端项目了
另外还可以将图片等文件配置成服务,比如 /home/foodie-shop/images 下有很多图片
location /images{
root /home/foodie-shop;
}
2
3
注:这里只是为了演示,因为这个目录在 / 下可以直接访问的 http://192.168.56.105:90/images/header-bg1.jpg
上述配置后,访问 http://192.168.56.105:90/images/header-bg1.jpg,它打开的文件是 /home/foodie-shop/images/header-bg1.jpg
这种方式需要注意的是:root + location + 请求的资源链接起来要是一个主机上存在的物理路径。
那么还可以使用 别名(alias) 的方式进行映射,如下所示
# 配置路由规则
location /i2 {
# 资源所在的物理路径
alias /home/foodie-shop/images;
}
2
3
4
5
访问路径变成了 http://192.168.56.105:90/i2/header-bg1.jpg,也就是说 /i2 会被转成 /home/foodie-shop/images 最后拼接成完成的资源物理路径
# 使用 Gzip 压缩提升传输效率
访问网站首页,按 size 倒序排列,看到最大的一个文件是 css 文件,我们使用压缩在降低它的大小
在 http 指令块中增加配置
http {
...
# 开启 gzip 压缩功能,目的:提高传输效率,节约带宽
gzip on;
# 限制最小压缩,小于 1 字节的文件不会压缩
gzip_min_length 1;
# 定义压缩级别(压缩比例)
gzip_comp_level 3;
# 定义需要压缩的文件类型
gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
重新加载配置后,查看效果
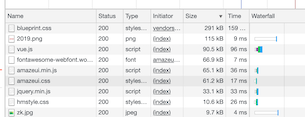
可以看到从 344 KB 压缩成了 61.2 KB
# location 匹配规则解析
# 默认匹配
默认的规则,比如请求 http://192.168.56.105:90/ 是可以访问到网站首页的
location / {
root /home/foodie-shop/;
index index.html;
}
2
3
4
# 精准匹配
location = / {
root /home/foodie-shop/;
index index.html;
}
2
3
4
这个规则,配置后,就访问不到网站首页了,因为只会匹配 / 但是这里会找 index.html
location = /index.html {
root /home/foodie-shop/;
index index.html;
}
2
3
4
这样配置后,就可以访问到网站首页了,但是其他的资源不能访问,因为只匹配了 index.html
# 正则匹配
# 波浪符号开头表示使用正则表达式
# * 表示不区分大小写
# \. 转义 . 号元字符为普通字符
# 分组里面任意一种格式 都可以路由
location ~* \.(GIF|png|bmp|jpg|jpeg) {
root /home/foodie-shop/;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
上面配置了一个 root 的目录,对文件后缀进行路由,所以只要这样访问就能访问到 /home/foodie-shop/images 目录下的图片资源了
http://192.168.56.105:91/images/header-bg1.jpg
# 非正则匹配
location ^~ /images {
root /home/foodie-shop/;
}
2
3
^~:以某个字符路径开头的请求
~ 表示使用正则表达式,前面用 ^ 表示非正则,这个就感觉和普通的默认匹配类似了