# 归并排序
# 简单介绍
归并排序(merge sort)是利用 归并 的思想实现的排序方法,该算法采用经典的 分治(divide-and-conquer)策略 :
- 分(divide):将问题分成一些小的问题,然后递归求解
- 治(conquer):将分的阶段得到的各答案「修补」在一起
即:分而治之
# 基本思想
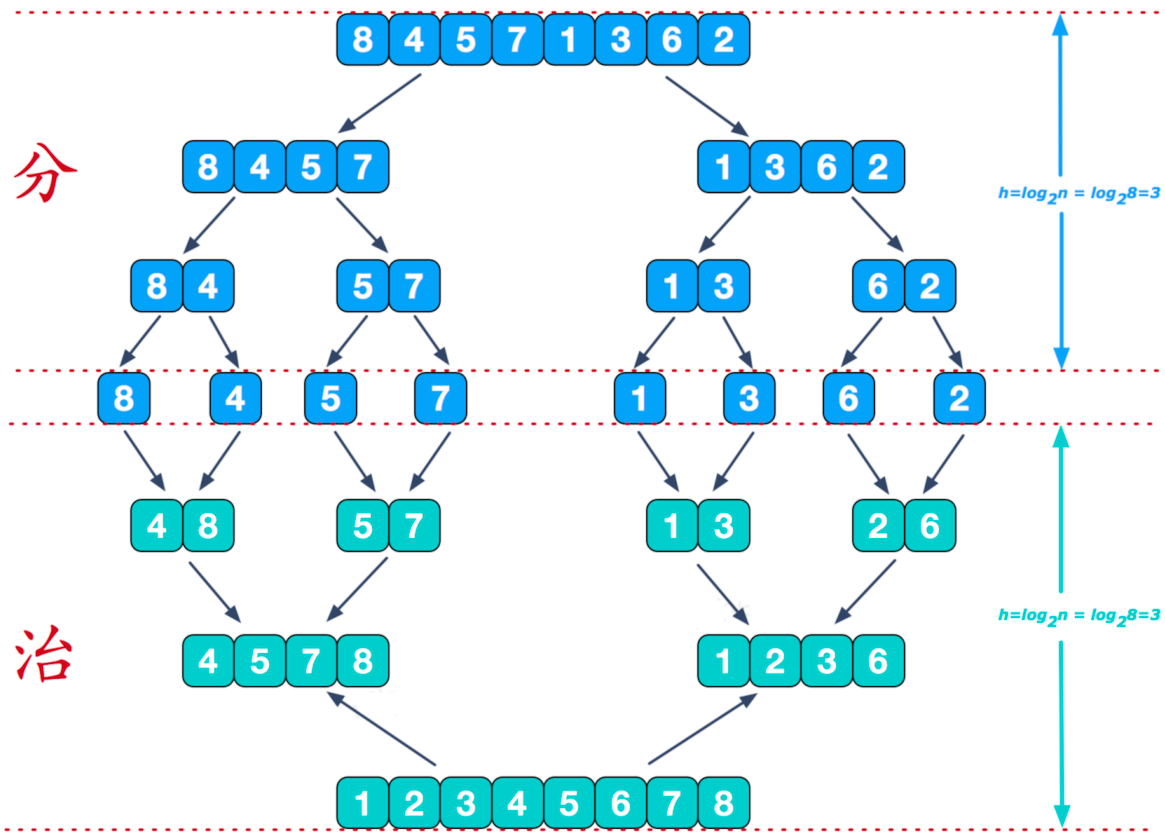
- 分:的过程只是为了分解
- 治:分组完成后,开始对每组进行排序,然后合并成一个有序序列,直到最后将所有分组合并成一个有序序列
可以看到这种结构很像一颗 完全二叉树,本文的归并排序我们采 用递归实现(也可采用迭代的方式实现)。分阶段 可以理解为就是递归拆分子序列的过程。
# 思路分析
对于分阶段相对较简单,下面着重来对治阶段进行分析。
合并相邻有序子序列分析:下图以 归并排序的最后一次合并 为例来分析,即对应上图的 [4,5,7,8] 和 [1,2,3,6] 两个已经有序的子序列合并为最终序列 [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8],下图展示了实现步骤
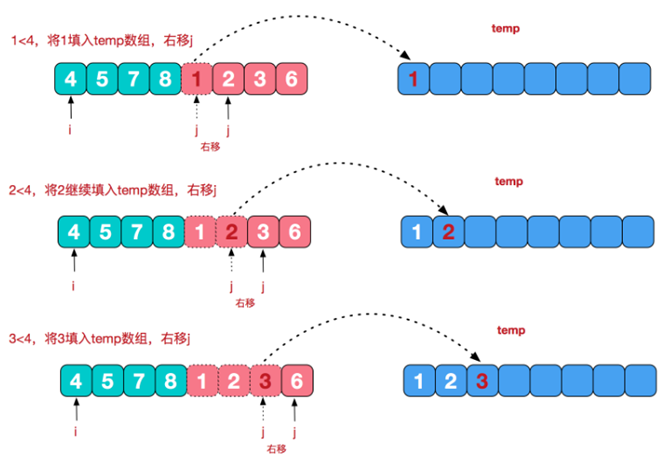
如图所示:这是最后一次的合并 操作,是两个有序序列。
- 从有序序列开始挨个比较,这里比较 4 和 1,1 < 4,那么 1 进入临时数组中,并且将自己的指针右移动一位
- 由于上一次 4 大于 1,指针并未移动,然后 4 和 2 对比,2 < 4 , 2 进入到临时数组中,并且将自己的指针右移动一位
- ...
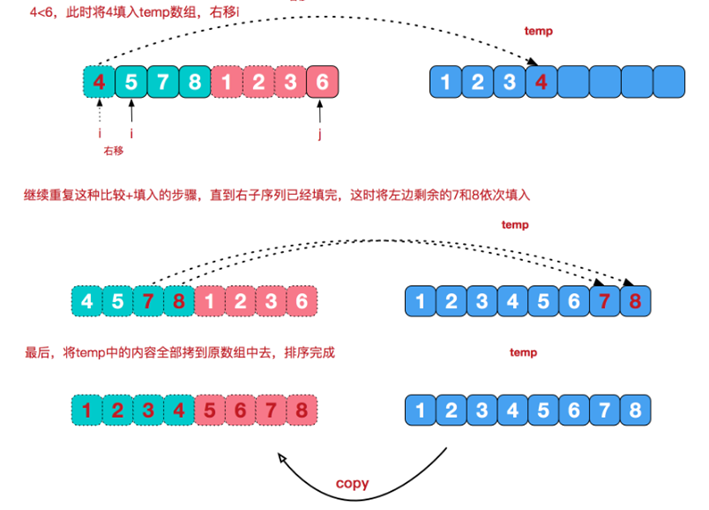
- 如果某一组已经全部进入了临时数组,那么剩余一组的剩余有序序列直接追加到临时数组中
- 最后,将 temp 内容拷贝到原数组中去,完成排序
# 代码实现
# 模仿实现
按照老师的讲解进行模仿实现,代码与视频中讲解的基本一致
先实现合并方法,这个是该算法中最重要的
/**
* <pre>
* 最难的是合并,所以可以先完成合并的方法,此方法请参考 基本思想 和 思路分析中的图解来完成
*
* </pre>
*
* @param arr 要排序的原始数组
* @param left 因为是合并,所以要得到左右两边的的数组信息,这个是左侧数组的第一个索引值
* @param mid 因为是一个数组,标识是第一个数组的最后一个索引,即 mid+1 是右侧数组的第一个索引
* @param right 右侧数组的结束索引
* @param temp 临时空间
*/
public void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) {
// 1. 按规则将两个数组合并到 temp 中
// 定时临时变量,用来遍历数组比较
int l = left; // 左边有序数组的初始索引
int r = mid + 1; // 右边有序数组的初始索引
int t = 0; // temp 数组中当前最后一个有效数据的索引
// 因为是合并两个数组,所以需要两边的数组都还有值的时候才能进行比较合并
while (l <= mid && r <= right) {
// 如果左边的比右边的小,则将左边的该元素填充到 temp 中
// 并移动 t++,l++,好继续下一个
if (arr[l] < arr[r]) {
temp[t] = arr[l];
t++;
l++;
}
// 否则则将右边的移动到 temp 中
else {
temp[t] = arr[r];
t++;
r++;
}
}
// 2. 如果有任意一边的数组还有值,则依序将剩余数据填充到 temp 中
// 如果左侧还有值
while (l <= mid) {
temp[t] = arr[l];
t++;
l++;
}
// 如果右侧还有值
while (r <= right) {
temp[t] = arr[r];
t++;
r++;
}
// 3. 将 temp 数组,拷贝到原始数组
// 注意:只拷贝当前有效数据到对应的原始数据中
int tempL = left; // 从左边开始拷贝
t = 0; // temp 中的有效值,可以通过下面的 right 判定,因为合并两个数组到 temp 中,最大值则是 right
/*
* 对于 8,4,5,7,1,3,6,2 这个数组,
* 从栈顶开始合并:8,4 | 5,7 1,3 | 6,2
* 先左递归的话:
* 第一次:8,4 合并:tempL=0,right=1
* 第二次:5,7 合并:tempL=2,right=3
* 第三次:4,8 | 5,7 进行合并,tempL=0,right=3
* 直到左递归完成,得到左侧一个有序的序列:4,5,7,8 然后开始右递归
* 最后回到栈底分解成两个数组的地方,将两个数组合并成一个有序数组
*/
System.out.println("tempL=" + tempL + "; right=" + right);
while (tempL <= right) {
arr[tempL] = temp[t];
tempL++;
t++;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
需要注意的是:这个图一定要看明白:
- 一直分解,到栈定首次合并时,是两个数字,也就是说,左侧数组只有一个数字,右侧数组只有一个数字
- 左侧数组只有一个数字时,left=0,right=1,那么 mid=0,边界判定时要用 left <= mid ,否则就会跳过对比合并了

完整代码如下
@Test
public void sortTest() {
int[] arr = new int[]{8, 4, 5, 7, 1, 3, 6, 2};
int[] temp = new int[arr.length];
mergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, temp);
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
/**
* 分 和 合并
*/
public void mergeSort(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
// 先分解左侧
mergeSort(arr, left, mid, temp);
// 再分解右侧
mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, right, temp);
// 最后合并
// 由于是递归,合并这里一定是栈顶的先执行
// 第一次:left = 0,right=1
// 第二次:left = 2,right=3
// 第三次:left = 0,right=3
// System.out.println("left=" + left + ";right=" + right);
merge(arr, left, mid, right, temp);
}
}
/**
* <pre>
* 最难的是合并,所以可以先完成合并的方法,此方法请参考 基本思想 和 思路分析中的图解来完成
*
* </pre>
*
* @param arr 要排序的原始数组
* @param left 因为是合并,所以要得到左右两边的的数组信息,这个是左侧数组的第一个索引值
* @param mid 因为是一个数组,标识是第一个数组的最后一个索引,即 mid+1 是右侧数组的第一个索引
* @param right 右侧数组的结束索引
* @param temp 临时空间
*/
public void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) {
// 1. 按规则将两个数组合并到 temp 中
// 定时临时变量,用来遍历数组比较
int l = left; // 左边有序数组的初始索引
int r = mid + 1; // 右边有序数组的初始索引
int t = 0; // temp 数组中当前最后一个有效数据的索引
// 因为是合并两个数组,所以需要两边的数组都还有值的时候才能进行比较合并
while (l <= mid && r <= right) {
// 如果左边的比右边的小,则将左边的该元素填充到 temp 中
// 并移动 t++,l++,好继续下一个
if (arr[l] < arr[r]) {
temp[t] = arr[l];
t++;
l++;
}
// 否则则将右边的移动到 temp 中
else {
temp[t] = arr[r];
t++;
r++;
}
}
// 2. 如果有任意一边的数组还有值,则依序将剩余数据填充到 temp 中
// 如果左侧还有值
while (l <= mid) {
temp[t] = arr[l];
t++;
l++;
}
// 如果右侧还有值
while (r <= right) {
temp[t] = arr[r];
t++;
r++;
}
// 3. 将 temp 数组,拷贝到原始数组
// 注意:只拷贝当前有效数据到对应的原始数据中
int tempL = left; // 从左边开始拷贝
t = 0; // temp 中的有效值,可以通过下面的 right 判定,因为合并两个数组到 temp 中,最大值则是 right
/*
* 对于 8,4,5,7,1,3,6,2 这个数组,
* 从栈顶开始合并:8,4 | 5,7 1,3 | 6,2
* 先左递归的话:
* 第一次:8,4 合并:tempL=0,right=1
* 第二次:5,7 合并:tempL=2,right=3
* 第三次:4,8 | 5,7 进行合并,tempL=0,right=3
* 直到左递归完成,得到左侧一个有序的序列:4,5,7,8 然后开始右递归
* 最后回到栈底分解成两个数组的地方,将两个数组合并成一个有序数组
*/
System.out.println("tempL=" + tempL + "; right=" + right);
while (tempL <= right) {
arr[tempL] = temp[t];
tempL++;
t++;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
测试输出
tempL=0; right=1
tempL=2; right=3
tempL=0; right=3
tempL=4; right=5
tempL=6; right=7
tempL=4; right=7
tempL=0; right=7
排序后:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
从这里也可以看到,先左递归的话,可以看到最开始合并的索引是 0,1 也就是在栈顶开始首次递归时:数组中只有一个数字。
最后一次合并:则是回到了最初栈底开始分解的放,将两个数组 0,7 进行排序的 temp 填充。完成了排序 。
8 个数字,会进行 7 次 合并
# 默写实现
自己根据上述所讲的基本思想和思路分析,按记忆进行默写实现。为了巩固记忆。
代码有部分可能会按照自己的习惯进行改写优化
/**
* 为了巩固记忆,自己根据基本思想进行默写实现
*/
public class MyMergeSortTest {
@Test
public void sortTest() {
int[] arr = new int[]{8, 4, 5, 7, 1, 3, 6, 2};
mergeSort(arr);
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public void mergeSort(int arr[]) {
int[] temp = new int[arr.length];
doMergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, temp);
}
/**
* 分治 与 合并
*
* @param arr
* @param left
* @param right
* @param temp
*/
private void doMergeSort(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
// 当还可以分解时,就做分解操作
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
// 先左递归分解
doMergeSort(arr, left, mid, temp);
// 再右递归分解
doMergeSort(arr, mid + 1, right, temp);
// 左递归分解到栈顶时,其实也是分为左右数组
// 左右都到栈顶时,开始合并:
// 第一次:合并的是 0,1 的索引,分解到最后的时候,其实只有一个数为一组,所以第一次合并是合并两个数字
merge(arr, left, mid, right, temp);
}
}
/**
* 开始合并,每次合并都是两组,第一次合并是两个数字,左右一组都只有一个数字
*
* @param arr
* @param left
* @param mid
* @param right
* @param temp
*/
private void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) {
// 1. 按照规则,将 temp 数组填充
// 2. 当任意一边填充完成后,剩余未填充的依次填充到 temp 数组中
// 3. 将 temp 数组的有效内容,拷贝会原数组,也就是将这次排序好的数组覆盖回原来排序的原数组中
int l = left; // 左侧数组初始索引
int r = mid + 1; // 右侧数组初始索引
int t = 0; // 当前 temp 中有效数据的最后一个元素索引
// 1. 按照规则,将 temp 数组填充
// 当两边都还有数字可比较的时候,进行比较,然后填充 temp 数组
// 只要任意一边没有数值可用时,就仅需到下一步骤
while (l <= mid && r <= right) {
// 当左边比右边小时,则填充到 temp 数组中
if (arr[l] < arr[r]) {
// 赋值完成后,t 和 l 都需要 +1,往后移动一个位置
// t++ 是先把 t 进行赋值,再进行 t+1 操作
temp[t++] = arr[l++];
} else {
// 当不满足时,则说明 右侧数字比左侧的小,进行右侧的填充
temp[t++] = arr[r++];
}
}
// 2. 有可能有其中一边会有剩余数字未填充到 temp 中,进行收尾处理
while (l <= mid) {
temp[t++] = arr[l++];
}
while (r <= right) {
temp[t++] = arr[r++];
}
// 3. 将这个有序数组,覆盖会原始排序的数组中
t = 0;
int tempL = left; // 从左侧开始,到右侧结束,就是这一次要合并的两组数据
// System.out.println("tempL=" + tempL + "; right=" + right);
while (tempL <= right) {
arr[tempL++] = temp[t++];
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
# 大数据量耗时测试
/**
* 大量数据排序时间测试
*/
@Test
public void bulkDataSort() {
int max = 80_000;
// max = 8;
int[] arr = new int[max];
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 80_000);
}
if (arr.length < 10) {
System.out.println("原始数组:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
Instant startTime = Instant.now();
int[] temp = new int[arr.length];
mergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, temp);
if (arr.length < 10) {
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
Instant endTime = Instant.now();
System.out.println("共耗时:" + Duration.between(startTime, endTime).toMillis() + " 毫秒");
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
多次测试输出
共耗时:26 毫秒
共耗时:37 毫秒
共耗时:30 毫秒
共耗时:30 毫秒
1
2
3
4
2
3
4